Disclaimer:
Please be aware that the content herein is comprised of personal reflections, observations, and insights from our contributors. It is not necessarily exhaustive or authoritative, but rather reflects individual perspectives. While we aim for accuracy, we cannot guarantee the completeness or up-to-date nature of the content.
Images
Type of the Solution
Technology
Affected Sector
Households
Description of the solution
Heat pumps help improve air quality and reduce GHG emissions compared to conventional heating technologies. A heat pump uses technology similar to that found in an air conditioner. It extracts heat from a source, such as the surrounding air, geothermal energy stored in the ground, or nearby sources of water or waste heat from a factory. Because most of the heat is transferred rather than generated, heat pumps are far more efficient than conventional heating technologies such as boilers or electric heaters. Households with a heat pump also spend less on energy than those using a gas boiler. In addition, a large‚Äêscale switch to heat pumps can prevent other risks associated with fossil fuel combustion such as carbon monoxide from poorly serviced heating stoves and gas boilers.
Socio-economic effects
Improved indoor and outdoor air quality, cost-effectiveness
Type of Measure
3. mitigation measures
Type of sub-measure
5. (none)
Who led the solution
Private sector
Timescale of implementation
Short-term (up to 1 year)
Other Notes
For ****-****-****-****ity.
Links to the solution
 Consent to share form or official link.
Consent to share form or official link.

 3Good health and well-being
3Good health and well-being 13Climate action
13Climate action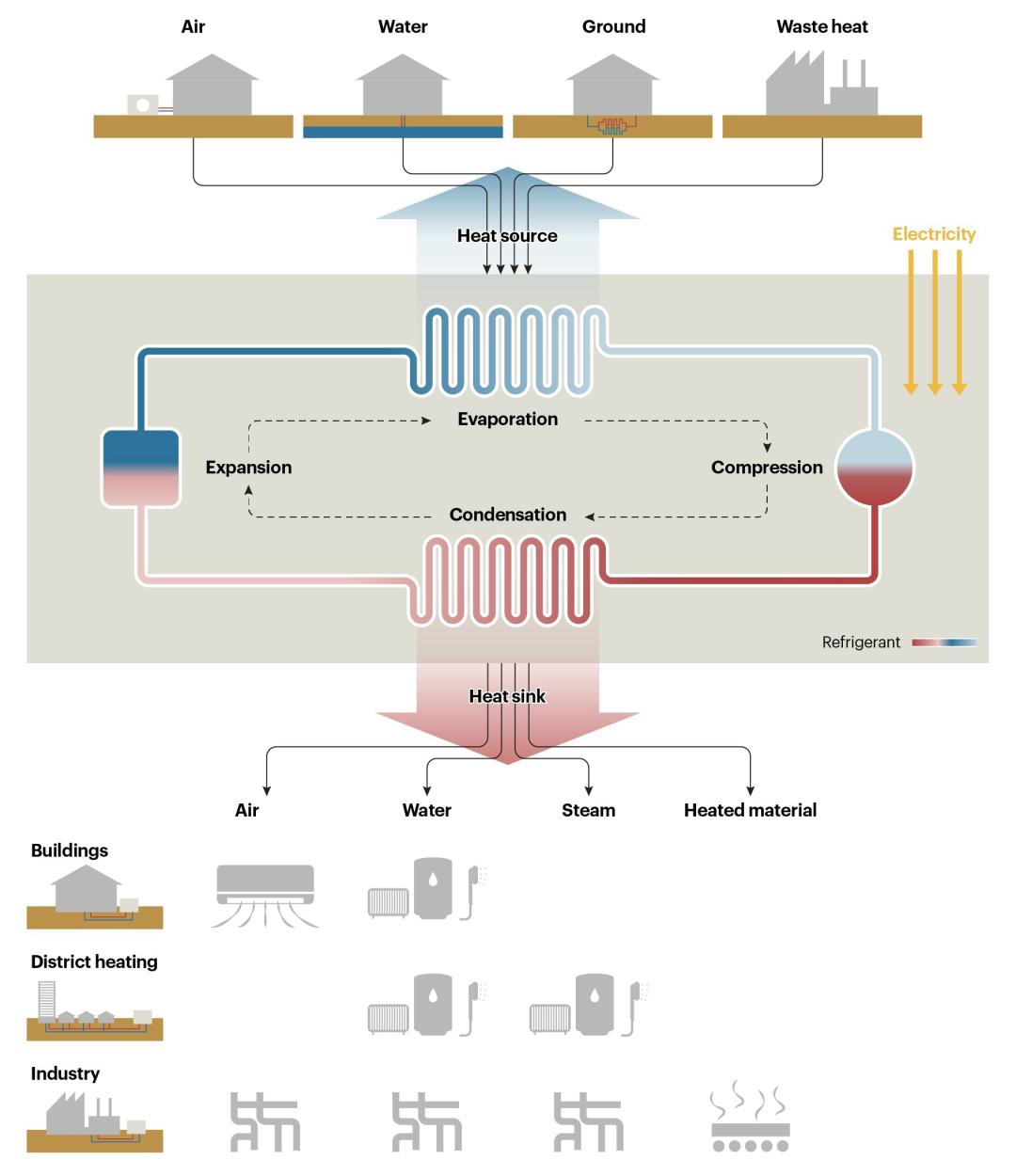
Comments
Log in to add a comment or reply.