Location(s)
Tags
SDG(s)
Sustainable Development Goal(s)
Powered by


SDG(s)
Sustainable Development Goal(s)
 6Clean water and sanitation
6Clean water and sanitation 9Industry, innovation and infrastructure
9Industry, innovation and infrastructurePlease be aware that the content herein has not been peer reviewed. It consists of personal reflections, insights, and learnings of the contributor(s). It may not be exhaustive, nor does it aim to be authoritative knowledge.
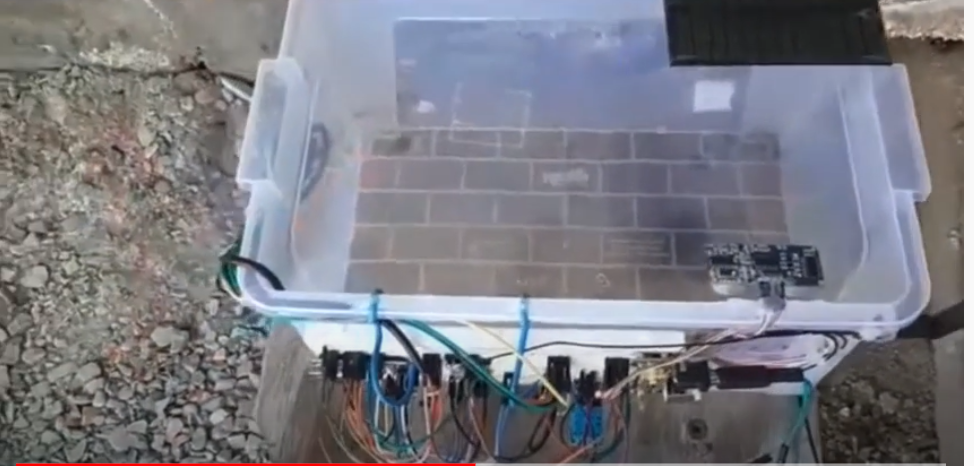

Comments
Log in to add a comment or reply.